Impulse and Change in Momentum
Impulse and Change in Momentum: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Linear Impulse, Linear Impulse of Constant Force, Linear Impulse of Time Varying Force, and Linear Impulse from F-T Diagrams.
Important Questions on Impulse and Change in Momentum
A ball of drops vertically on the floor with a speed of . It rebounds with a velocity of .
What impulse acts on the ball during contact?
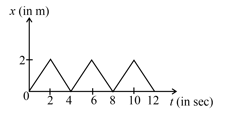
Figure shows the position–time graph of one dimensional motion of a body of mass . What is the time interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body?
A large force is acting on a body for a short time. The impulse imparted is equal to the change in _____.
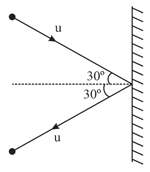
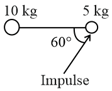
A ball of mass strikes a rigid wall with speed at an angle of with the normal and gets reflected with the same speed and at the same angle, as shown in the figure. If the ball is in contact with the wall for time , then the force experienced by the wall is:
If the force on a rocket, which ejects mass at a speed relative the rocket is , due to combustion of the fuel, then the rate of combustion of the fuel is
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by a given equation Newton. The initial velocity of the body is 10 m/s. The velocity of the body after 5 sec is
A body of mass 5 kg is acted on by a net force F which varies with time t as shown in graph, then the net momentum in SI units gained by the body at the end of 10 seconds is
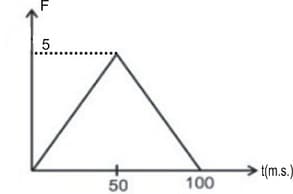
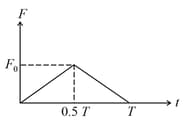
A body of has an initial speed . A force acts on it for in the direction of motion. The force-time graph is shown in figure. The final speed of the body after is
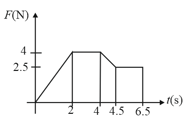
A ball of mass moving with a velocity rebounds from a wall. The collision is assumed to be elastic and the force of interaction between the ball and wall varies as shown in the figure. Then the value of is -
Two point masses connected by an ideal string are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the diagram. A sharp impulse of is given to the mass. The velocity of the mass will be -
A sping balance is adjusted at zero. Elastic collisions are brought about by dropping particles of one gram each on the pan of the balance. They recoil upwards without change in their speed. If the height of fall of particles is and the rate of particle dropping is per second, then the reading of the balance is (take )
A disc of mass is kept floating horizontally in the air by firing bullets, each of mass , with the same velocity at the same rate of bullets per second. The bullets rebound with the same speed in positive direction. The velocity of each bullet at the time of impact is
A player kicks a football of mass and the football begins to move with a velocity of . If the contact between the leg and the football lasts for Then the force on the ball should be
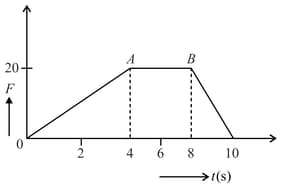
A force-time graph for a linear motion of a body is shown in the figure. The change in linear momentum between and is
A hockey player receives a corner shot at a speed of at an angle of with the -axis and then shoots the ball of mass 100 g along the negative -axis with a speed of . If it remains in contact with the hockey stick for 0.01 s, the force imparted to the ball in the -direction is
A unidirectional force varying with time as shown in the figure acts on a body initially at rest for a short duration. Then the velocity acquired by the body is
A rocket in free space expels of gas per second at exhaust velocity for seconds. What is the increase in the speed of rocket in this time (assume time interval is too small to consider variation in acceleration)
A ball of mass m is moving towards a batsman at a speed v. The batsman strikes the ball and deflects it by an angle without changing its speed. The impulse imparted to the ball is given by
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with a momentum of 10 kg m s –1. A force of 0.2 N acts on it in the direction of motion of body for 10 s. The increase in its kinetic energy is
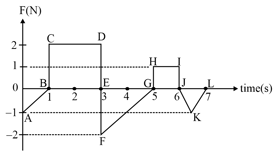
A force acts on an object (mass = 1 kg) which is initially at rest as shown in the figure. Draw graph showing the momentum of the object varying during the time for which the force acts.